Point in polygon problem
Known as Point-In-Polygon problem, testing whether a point lies inside a polygon is another classic literature problem in computational geometry.
As a prerequiste for this post, make sure to read Line segments intersection.
A simple test to check whether a point \( p=\{x,y\} \) lies inside a given polygon is to extend one of its dimensions to infinity
\[p_{inf} = \{ +\infty,y \}\]and do a line segments intersection test between \( \overline{p \ p_{inf}} \) and each one of the edges of the polygon. If the count of the intersections is odd, the point lies inside the polygon.
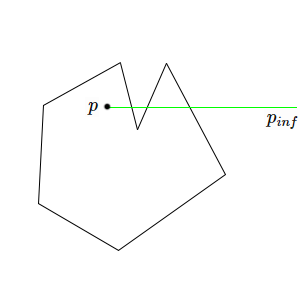
Special attention deserve two cases:
-
when segment \( \overline{p \ p_{inf}} \) has a successful intersection test and \( p \) is found collinear to the polygon edge: if \( p \) lies in the polygon edge segment, any further check can be skipped since the point lies on the border of the polygon
-
when the
to_infinitysegment crosses one or more vertices of the polygon the intersection has to be counted once (thanks B Soma Naik for spotting this)
Algorithm follows
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
// NB: max_int would cause overflow in the orientation test
const int INF = 100'000;
struct Point {
int x, y;
bool operator==(const Point& other) const {
return (x == other.x && y == other.y);
}
};
namespace std {
template <> struct hash<Point> {
size_t operator()(const Point& p) const {
return (p.x * 41) ^ p.y;
}
};
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Point& p) {
os << "{" << p.x << ";" << p.y << "}";
return os;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const vector<Point>& p) {
os << "{";
copy(p.begin(), p.end(), ostream_iterator<Point>(os));
os << "}";
return os;
}
int orientation(const Point& p1, const Point& p2, const Point& q1) {
int val = (p2.y - p1.y) * (q1.x - p2.x) - (q1.y - p2.y) * (p2.x - p1.x);
if (val == 0)
return 0;
else
return (val < 0) ? -1 : 1;
}
// Returns true if q lies on p1-p2
bool onSegment(const Point& p1, const Point& p2, const Point& q) {
if (min(p1.x, p2.x) <= q.x && q.x <= max(p1.x, p2.x)
&& min(p1.y, p2.y) <= q.y && q.y <= max(p1.y, p2.y))
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool intersectionTest(const Point& p1, const Point& p2,
const Point& p3, const Point& p4) {
int o1 = orientation(p1, p2, p3);
int o2 = orientation(p1, p2, p4);
int o3 = orientation(p3, p4, p1);
int o4 = orientation(p3, p4, p2);
// General case
if (o1 != o2 && o3 != o4)
return true;
// Special cases
if (o1 == 0 && onSegment(p1, p2, p3))
return true;
if (o2 == 0 && onSegment(p1, p2, p4))
return true;
if (o3 == 0 && onSegment(p3, p4, p1))
return true;
if (o4 == 0 && onSegment(p3, p4, p2))
return true;
return false;
}
bool pointInPolygon(const Point& p, const vector<Point>& polygon) {
if (polygon.size() < 3)
return false; // Flawed polygon
Point PtoInfinity = { INF , p.y };
int intersectionsCount = 0;
int i = 0, j = i + 1;
// Same Y coordinate points have to be counted once
std::unordered_set<Point> sameYcoordPoints;
do {
if (intersectionTest(p, PtoInfinity, polygon[i], polygon[j]) == true) {
bool invalidIntersection = false;
if (p.y == polygon[i].y || p.y == polygon[j].y) {
auto res = sameYcoordPoints.find(polygon[i]);
// Possible collision
if (res != sameYcoordPoints.end() && *res == polygon[i])
invalidIntersection = true;
res = sameYcoordPoints.find(polygon[j]);
// Possible collision
if (res != sameYcoordPoints.end() && *res == polygon[i])
invalidIntersection = true;
if (p.y == polygon[i].y)
sameYcoordPoints.emplace(polygon[i]);
else if (p.y == polygon[j].y)
sameYcoordPoints.emplace(polygon[j]);
}
if (!invalidIntersection) {
++intersectionsCount;
if (orientation(polygon[i], polygon[j], p) == 0) { // Collinear
if (onSegment(polygon[i], polygon[j], p) == true)
return true;
else {
// Exception case when point is collinear but not on segment
// e.g.
// * ************
// / \
// k w
// The collinear segment is worth 0 if k and w have the same
// vertical direction
int k = (((i - 1) >= 0) ? // Negative wraparound
(i - 1) % static_cast<int>(polygon.size()) :
static_cast<int>(polygon.size()) + (i - 1));
int w = ((j + 1) % polygon.size());
if ((polygon[k].y <= polygon[i].y && polygon[w].y <= polygon[j].y)
|| (polygon[k].y >= polygon[i].y && polygon[w].y >= polygon[j].y))
--intersectionsCount;
}
}
}
}
i = ((i + 1) % polygon.size());
j = ((j + 1) % polygon.size());
} while (i != 0);
return (intersectionsCount % 2 != 0);
}
int main() {
auto printPointInPolygon = [](auto p, auto& polygon) {
cout << boolalpha << "Point " << p << " lies in polygon " << polygon <<
" - " << pointInPolygon(p, polygon) << endl;
};
vector<Point> polygon = { { 2,1 },{ 3,2 },{ 2,3 } };
Point p = { 1,2 };
printPointInPolygon(p, polygon);
polygon = { { 0, 0 },{ 5, 0 },{ 10, 10 },{ 5, 10 } };
p = { 3, 3 };
printPointInPolygon(p, polygon);
p = { 4, 10 };
printPointInPolygon(p, polygon);
polygon = { { 0, 0 },{ -5, 0 },{ -10, -10 } };
p = { 0, -2 };
printPointInPolygon(p, polygon);
return 0;
}